Table Of Content
Also known as "white space," this design element uses space as part of the design. It can also use the other elements to create the illusion of added information, which tricks the eye into thinking something is there. The principle of design is concerned with what you add to your design. The only one that expressly deals with what you don't contribute is white space (or negative space).

Topics in This Article
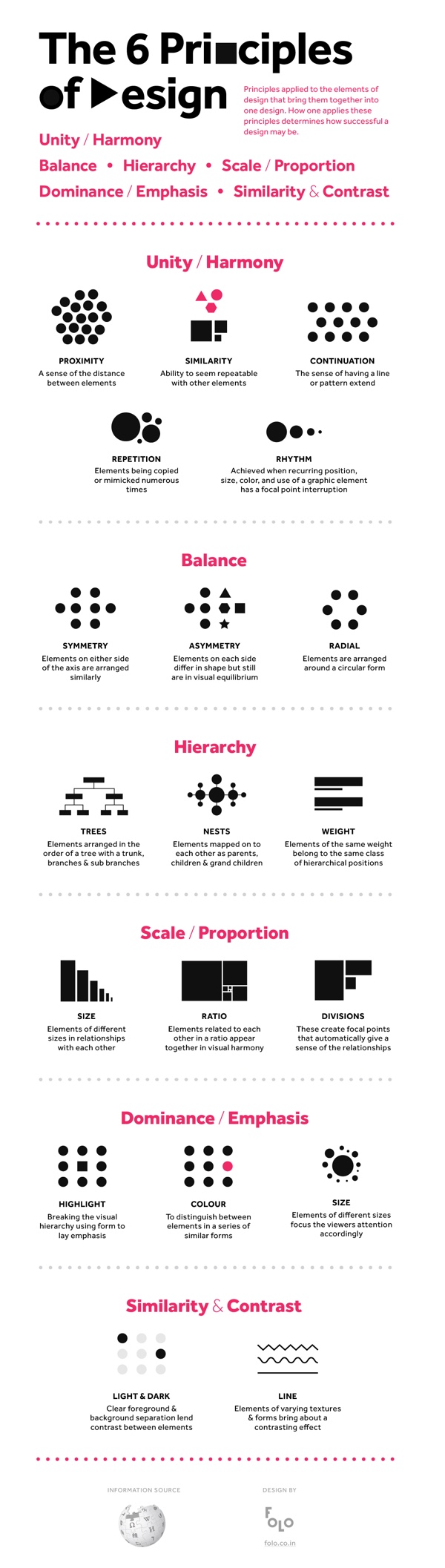
Repeating elements over and over again in the design creates better consistency and ease for the user to know what to do and where to find something. This is majorly a good principle to use for motion graphics while creating a motion video repeating hills and mountains continuously to avoid any breaks in visuals. In visual design, form is described as the way an artist arranges elements in the entirety of a composition.[5] It may also be described as any three-dimensional object. Form can be measured, from top to bottom (height), side to side (width), and from back to front (depth). It can be defined by the presence of shadows on surfaces or faces of an object. There are two types of form, geometric (artificial) and natural (organic form).
Hierarchy
A complete lack of contrast would result in a design that’s simply a single background color with no other visible elements — not exactly a functional design. A design where you can see different elements automatically has some level of contrast. It’s important to familiarize yourself with the most common eye movement patterns, F- and Z-patterns, and the layer cake pattern. F- and Z-patterns are more common on image-heavy pages, while the layer cake pattern is facilitated by lots of text with headings and subheadings. Emphasis is the part of a design that catches the eye of the user—a focal point, in other words.
The Role of Hierarchy in Guiding Viewer's Attention
By incorporating patterns into a design, designers can add visual interest, texture, and depth. In this course, you will gain a holistic understanding of visual design and increase your knowledge of visual principles, color theory, typography, grid systems and history. You’ll also learn why visual design is so important, how history influences the present, and practical applications to improve your own work. These insights will help you to achieve the best possible user experience.
Framework for Innovation - Design Council
Framework for Innovation.
Posted: Thu, 11 May 2023 08:34:55 GMT [source]
To make the relevant elements appear to be a group, proximity principles talk about adequate spacing between elements to help users visually combine or separate them from each other. Elements that are near to each other are often grounded together as one part, whereas a good amount of spacing between elements separates them from each other. In most text editors, there are a lot of options to edit or input text such as different heading sizes, paragraphs, quotes, and captions. All these styles should also be added to text while designing interfaces. It is also good to use different font styles(there are a lot of amazing font combinations) which can be used to create a good text hierarchy or balanced typography. A printed piece can be as small as a postage stamp or as large as a billboard.
visual design principles for web designers
Only then will you be able to defy these graphic design conventions and develop your unique style. The aspects listed above—particularly balance, alignment, and contrast —can help you achieve that aim, but your design will be doomed without adequate movement. The line is an element of art defined by a point moving in space.
How to Add Music to a Video in 4 Steps: Renderforest Guide 101
Apply our foundational visual design principles and leave coding behind - check out our Webflow tutorial to discover how you can start building design-first online experiences. You don’t need to sacrifice visual appeal for functionality or vice versa. It’s a delicate dance of give and take, a blend of art and science. Applying UX visual design principles doesn’t have to be overwhelming. In fact, by understanding a few core concepts, you can see immediate improvements in your design’s performance and user engagement. Rhythm in visual design refers to the repetition of visual elements to create a sense of movement, pattern, or tempo.
Colour theory is a branch of design focused on the mixing and usage of different colours in design and art. In colour theory, an important distinction exists between colours that mix subtractively and colours that mix additively. Just like when balancing weight, if you were to have one small design element and one large design element on the two sides of the axis, the design would feel a bit unbalanced. The area taken by the design element matters when creating balance, not just the number of elements.
Visual hierarchy is the guide that takes users by the hand and leads them through your design without a second thought. Balance is your zen master, ensuring everything feels just right, calm, and collected. That’s your spice, adding that essential zing that makes your design sing.
Unity in design principles refers to the cohesive arrangement of elements that ensures all parts of a composition work together harmoniously. It's achieved when each element appears to be an integral part of the overall design, resulting in a complete and aesthetically pleasing piece. In addition to setting a mode and tone and bringing out certain emotions, color also contributes to contrast, variety, harmony, repetition, and space. Because of these many roles, color choice can effectively make or break a design.
This blog will walk you through seven fundamental pointers of the design principle that can help you design a website UI or mobile apps professionally. All these are useful while creating different design compositions, both on paper and in Figma. Before getting to know the visual principles, let’s understand what it is actually about and why is it so important. If you see a fuzzy silhouette of a person walking far away at night, your brain knows right away it’s a person from the shape of the body and the individual limbs. You don’t need to see the hands or the eyes or the feet to know it’s a person, but these visual details help you determine who the person is.

No comments:
Post a Comment